7 Proven Ways Nutrition Boosts Mental Health During Depressive Episodes
Depression isn’t just about feeling sad; it’s about low energy, poor focus, and the sense that even simple tasks take monumental effort. And while therapy and medication are often part of recovery, there’s another piece of the puzzle most people overlook: what you eat every day.
Research shows that the right nutrition can reduce depressive symptoms, balance brain chemistry, and even make other treatments work better. Combine that with evidence-based options like Deep TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation), and you’ve got a stronger, multi-layered approach to fighting depression.
Let’s break down exactly how food influences your mood and how you can use nutrition alongside advanced treatments to regain control.
1. Stop the Blood Sugar Rollercoaster
Most people don’t realize how much a “normal” meal can affect their mood. A plate piled with polished rice, a few biscuits with evening chai, or a sugary drink when you’re tired; these quick fixes spike blood sugar fast. But the crash that follows leaves you foggy, restless, and emotionally flat.
When blood sugar drops, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones were designed to keep us alert in danger, but in daily life they fuel irritability, anxiety, and mood swings. For someone managing depression, that cycle makes the lows even heavier.
What you can do instead:
- Choose slow-digesting carbs like millets, oats, quinoa, or brown rice.
- Pair carbs with protein and healthy fats: dal with rice, peanut butter on fruit, or curd with whole grains.
- Don’t skip breakfast: starting the day with eggs, upma, or sprouts helps keep sugar steady.
- Cut back on sugary drinks: swap colas and packaged juices for lemon water, buttermilk, or green tea.
Keeping blood sugar steady won’t erase depression, but it reduces the extra stress your body doesn’t need. It also makes advanced treatments like Deep TMS more effective, since the brain works best when its energy supply is stable.

2. Lower Inflammation to Protect Your Mind
Chronic inflammation isn’t just about aches or stomach trouble it directly affects brain chemistry. It interferes with serotonin and dopamine, the neurotransmitters responsible for mood, motivation, and emotional balance.
One of the most effective anti-inflammatory diets is the Mediterranean style of eating is built on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats like olive oil. Multiple studies show it lowers rates of depression compared to processed-food-heavy diets.
Add these anti-inflammatory foods to your meals:
- Leafy greens like spinach, methi, or kale
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, or sardines
- Olive oil, nuts, and seeds
- Fresh fruits especially berries, oranges, and pomegranate
Even small swaps like using olive oil instead of refined oil, or having roasted chana instead of fried snacks; make a measurable difference over time.

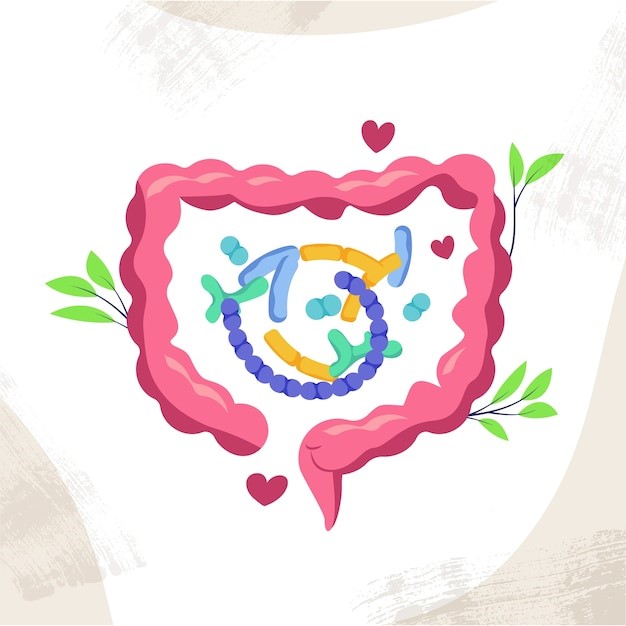
3. Heal Your Gut—Your “Second Brain”
Ever noticed how stress gives you stomach trouble or how eating badly for a week leaves you feeling low and sluggish? That’s the gut-brain connection at work.
Your gut microbiome trillions of bacteria living in your digestive system communicates constantly with your brain. Over 90% of serotonin is made in the gut, not the brain. When gut bacteria are healthy, they send positive signals that regulate mood. When they’re imbalanced (because of processed foods, stress, or antibiotics), those signals turn negative, fueling anxiety and depression.
Ways to build a gut-friendly diet:
- Probiotics: yogurt, kefir, idli/dosa batter (naturally fermented), kimchi, sauerkraut
- Prebiotics: garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, whole pulses
Fiber-rich foods: beans, lentils, oats, and fresh vegetables
Think of your gut like fertile soil. Feed it right, and your “mental health garden” grows stronger.

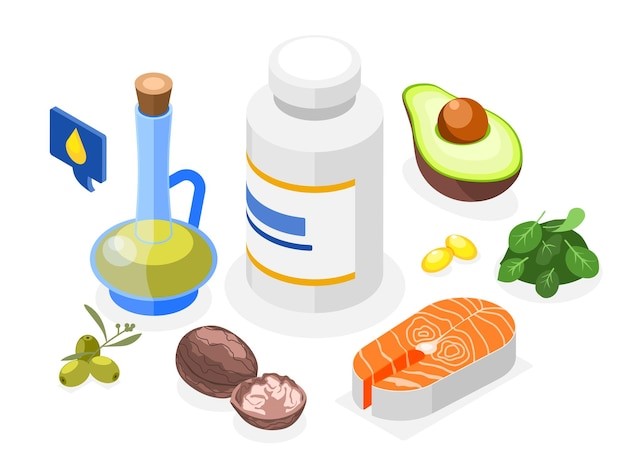
4. Load Up on Mood-Boosting Nutrients
Certain nutrients are like switches for brain health without them, your mood regulation system simply doesn’t work at full capacity.
Here are the essentials:
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Reduce inflammation and boost emotional balance. Found in salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds.
-
Vitamin D – Low levels are strongly linked to depression. Sources: sunlight, fatty fish, eggs.
-
Selenium – Helps calm anxiety and support brain health. A few Brazil nuts a week are enough.
-
B Vitamins (especially B12 and folate) – Critical for neurotransmitter production. Found in leafy greens, legumes, eggs, and poultry.
-
Zinc – Deficiency is common in people with depression. Best sources: pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, red meat.
-
Antioxidants (A, C, E) – Protect brain cells from oxidative stress. Add colorful vegetables and fruits daily.
-
Tryptophan (amino acid) – Converts to serotonin. Sources: turkey, cheese, sesame seeds, legumes.
Making meals nutrient-dense isn’t about complicated recipes. It’s about building a plate with variety; something our traditional Indian thalis already do well.

5. Cut the Hidden Mood Killers
Some foods and drinks quietly sabotage your mental health, especially when consumed regularly.
-
Alcohol: A depressant that disrupts sleep and serotonin balance.
-
Caffeine (in excess): One cup of chai or coffee is fine, but too much leads to jitteriness, anxiety, and insomnia.
-
Ultra-processed foods: Instant noodles, packaged snacks, sugary cereals which are loaded with trans fats and additives that trigger inflammation.
Reducing these doesn’t mean eliminating joy from your diet. It’s about balance. Even cutting them by half can improve sleep, mood, and energy.

6. Don’t Fall Into the Comfort Food Trap
Depression often pushes you to crave “comfort foods”; fried pakoras, sweets, or greasy takeout. They give a temporary dopamine boost, but the crash afterward makes symptoms worse.
Smarter comfort swaps:
-
Dark chocolate (70% or higher) instead of milk chocolate
-
Roasted makhana or peanuts instead of chips
-
Homemade smoothies with berries and yogurt instead of bottled sodas
-
Grilled paneer or chicken tikka instead of deep-fried snacks
This isn’t about denying comfort; it’s about choosing foods that comfort you and support your mental health.

7. Combine Nutrition with Advanced Treatments
Here’s the truth: nutrition alone won’t cure depression. But it does give your brain the raw materials it needs to function better. And when combined with modern therapies like Deep TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation), the results are much stronger.
Deep TMS is a non-invasive treatment that stimulates specific brain regions linked to mood regulation. It’s FDA-approved, safe, and particularly effective for people who haven’t responded well to medication.
Think of it like this:
-
Nutrition stabilizes your foundation.
-
Deep TMS rewires and activates the brain areas struggling in depression.
Together, they create a holistic, science-backed approach that addresses both the biological and lifestyle sides of mental health.
Depression is complex but your daily food choices play a bigger role than most people realize. By stabilizing blood sugar, lowering inflammation, healing your gut, and fueling your body with key nutrients, you give your brain the environment it needs to heal.
When you combine these nutrition strategies with advanced treatments like Deep TMS, you’re not just fighting depression; you’re building resilience, focus, and long-term stability.
Start small. One change in your meals. One swap at snack time. One choice to support your brain. Over time, these small steps add up to real progress.